SEO-Friendly Website Structure: Hosting & Technical Setup Guide


Creating an SEO-friendly website structure is not just about neat navigation. It directly affects how search engines crawl your site, distribute authority, and understand your content. If your structure is confusing, too deep, or technically flawed, rankings will struggle, no matter how strong your content is.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to build a search-optimised architecture from the ground up — including hierarchy, URLs, internal linking, hosting setup, technical configurations, and performance optimisation.
What Is an SEO-Friendly Website Structure?
An SEO-friendly website structure is a logical, organised framework that helps search engines and users navigate your website efficiently. It determines:
- How pages are grouped
- How authority flows
- How easily bots can crawl
- How quickly content is indexed
Search engines rely on internal links, URL structure, and site hierarchy to understand topical relevance. When structured properly, your website becomes easier to crawl, index, and rank.
Core principles include:
- Clear hierarchy (Homepage → Categories → Subcategories → Pages)
- Logical internal linking
- Minimal crawl depth
- Clean URLs
- Fast and secure hosting
Why Website Structure Matters for SEO Rankings

1. Crawl Efficiency
Search engines have a crawl budget. If your site has excessive depth, broken links, or redirect chains, bots waste resources. A well-structured site ensures important pages are discovered quickly.
2. Indexation Control
Poor structure leads to duplicate pages, parameter URLs, and orphan content. Proper hierarchy and canonical tags improve index accuracy.
3. Link Equity Distribution
Internal linking spreads authority from high-performing pages to deeper content. This improves rankings for commercial and informational pages alike.
4. User Experience Signals
Bounce rate, dwell time, and engagement influence SEO performance. A logical structure improves navigation and increases session duration.
5. Core Web Vitals Impact
Hosting quality influences page speed and structural efficiency. If your server response time is slow, structure alone won’t save you. See how hosting affects rankings.
Ideal Website Hierarchy: Flat vs Deep Structure
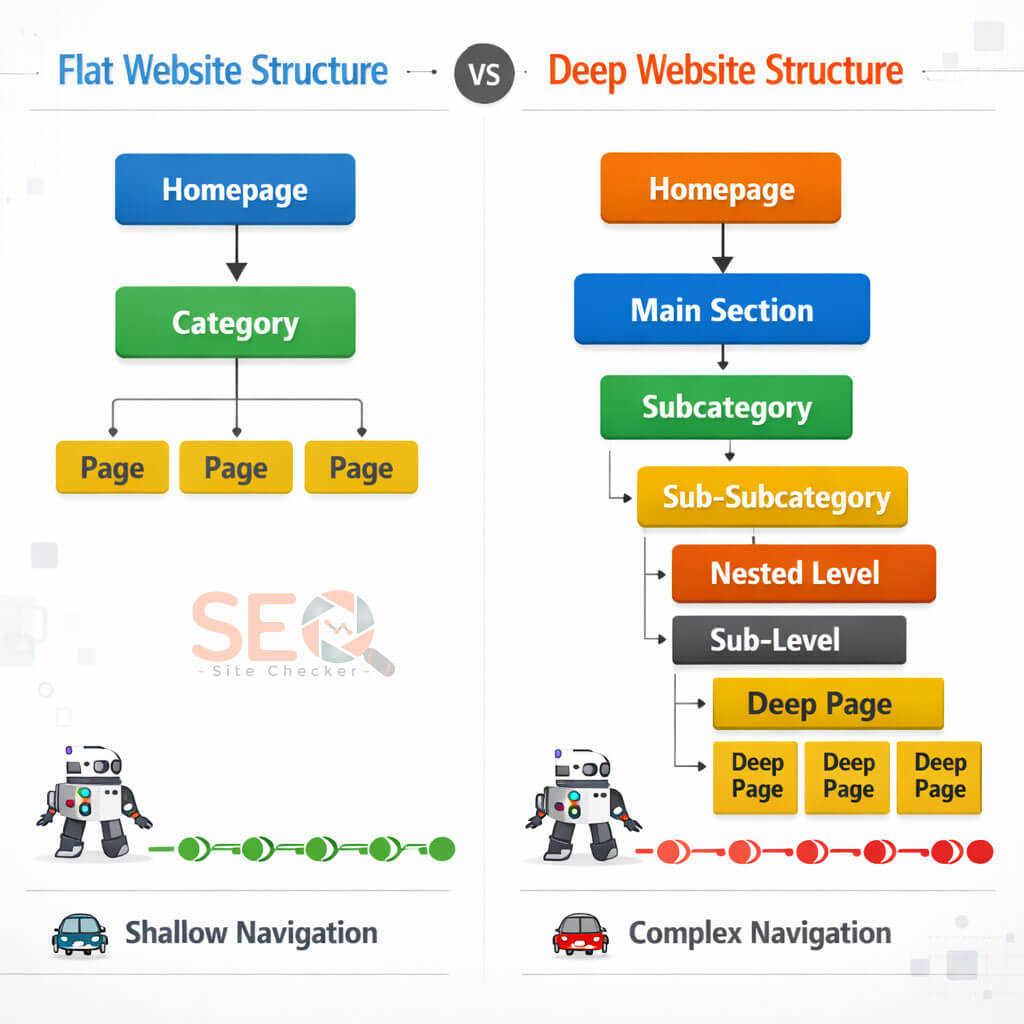
Flat Structure (Recommended)
A flat architecture ensures most pages are accessible within 3 clicks from the homepage.
Example:
Homepage
→ Category
→ Subcategory
→ Content Page
This improves crawl efficiency and distributes authority evenly.
Deep Structure (Avoid)
Homepage
→ Category
→ Subcategory
→ Sub-subcategory
→ Nested Folder
→ Page
Excessive depth reduces crawl frequency and delays indexing.
Silo Structure & Topic Clusters
Group related content under clear thematic categories. This improves semantic relevance and strengthens topical authority.
For example:
SEO Category
→ Technical SEO
→ Website Structure
→ Hosting Optimization
SEO-Friendly URL Structure Best Practices
Your URL structure must reflect your hierarchy.
Best Practices
- Keep URLs short and descriptive
- Include primary keyword naturally
- Avoid dynamic parameters
- Use hyphens, not underscores
- Maintain HTTPS
- Implement canonical tags
Example of good URL:
example.com/seo-friendly-website-structure/
Avoid:
example.com/category?id=234&ref=seo
Navigation Structure for SEO
Navigation defines crawl pathways.
Primary Navigation
- Clear categories
- Avoid overcrowding
- Link to important revenue pages
Footer Navigation
- Link to essential pages
- Include sitemap link
- Avoid keyword stuffing
Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumb navigation improves user experience and helps search engines understand hierarchy. Add breadcrumb schema markup for enhanced SERP display.
HTML Sitemap
An HTML sitemap improves discoverability for users and bots.
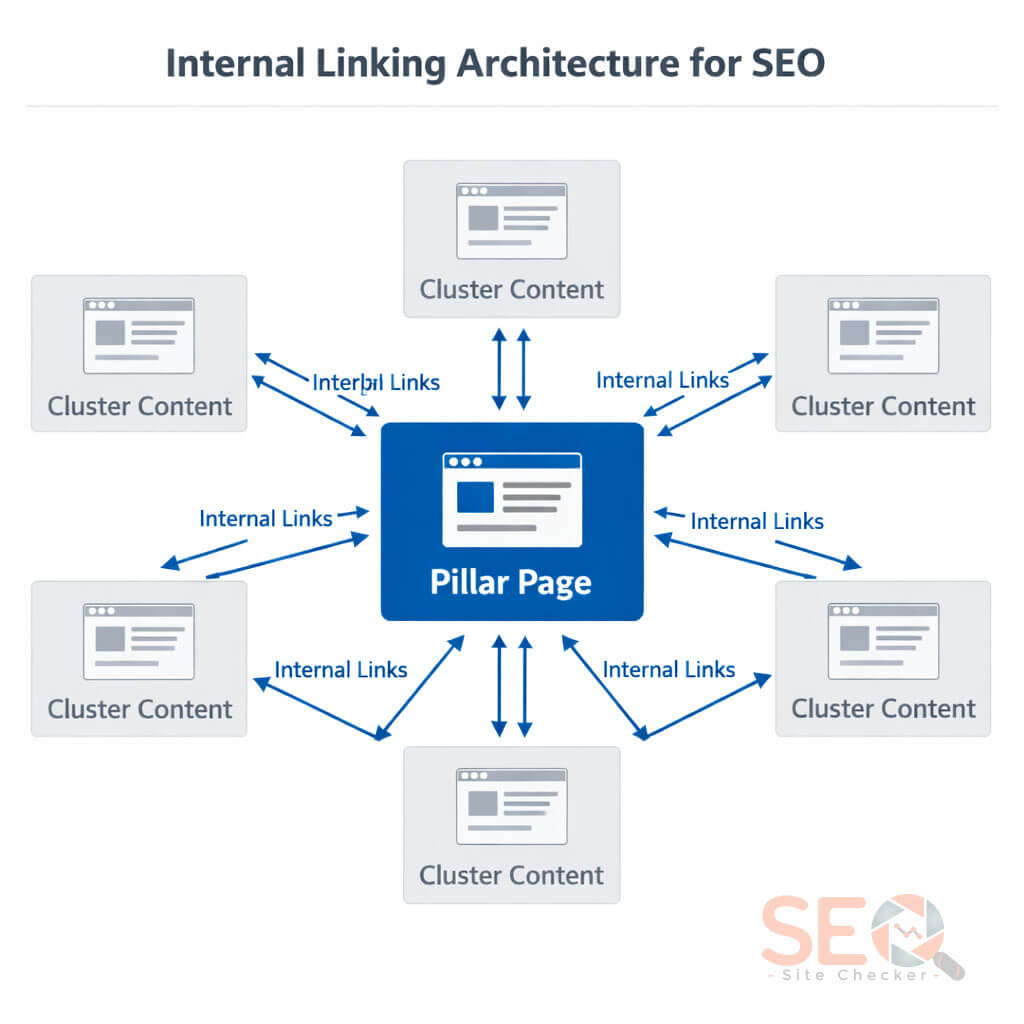
Internal Linking Architecture
Internal linking is one of the most powerful structural ranking factors.
Best Practices
- Use contextual links within content
- Avoid generic anchor text
- Link to cornerstone pages
- Fix orphan pages
- Keep important pages within 3 clicks
For hosting-related architecture optimisation, review: Best Web Hosting for SEO in 2026
And for performance comparisons: Cloud Hosting vs Shared Hosting - Which Is Better for SEO?
Technical Setup for SEO-Friendly Structure
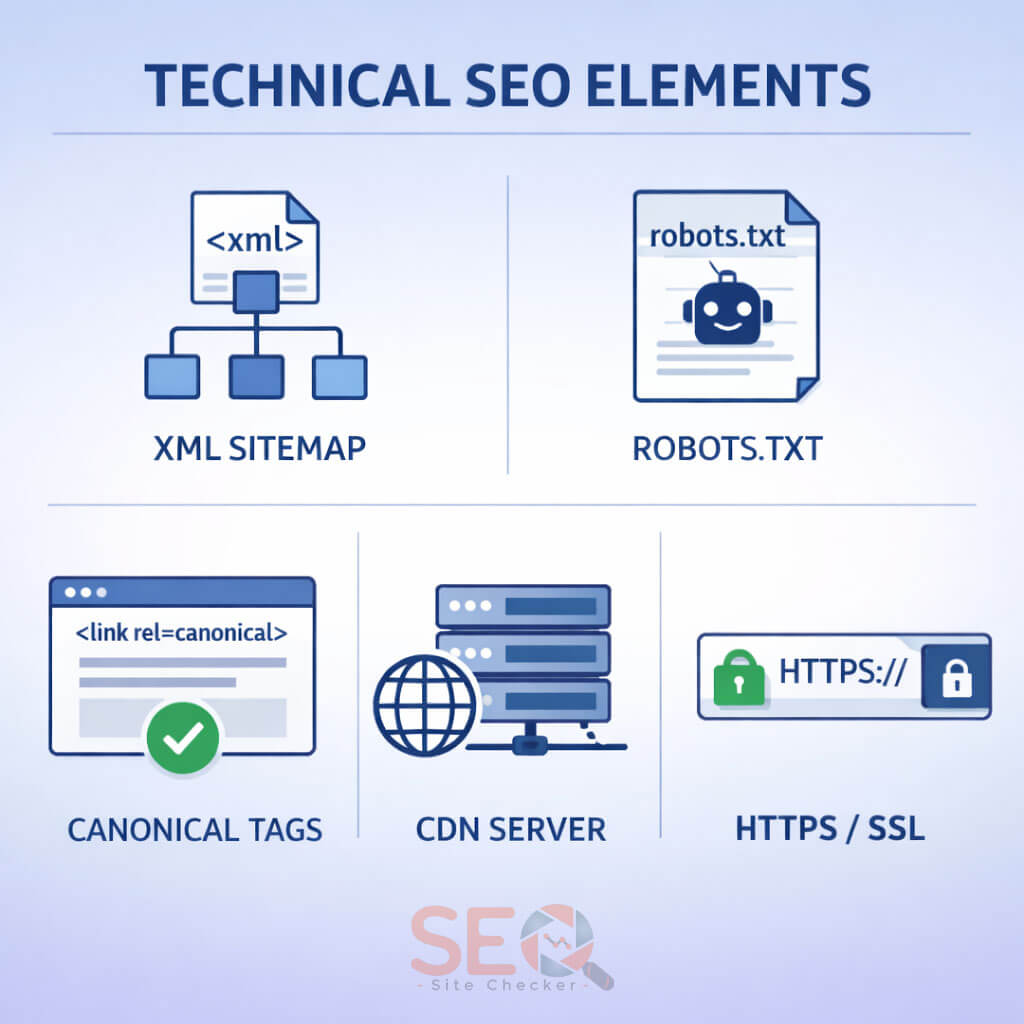
Structure without technical optimisation will underperform.
XML Sitemap
- Submit via Google Search Console
- Include canonical URLs only
- Update automatically
Refer to Google’s official site structure guidelines from Google Search Central for updated best practices.
Robots.txt
- Allow important directories
- Block thin or duplicate pages
- Avoid blocking CSS/JS files
Canonical Tags
Prevent duplicate content issues across category pages and filtered URLs.
Structured Data
Implement schema for:
- Breadcrumb
- FAQ
- Article
- Product (if applicable)
Hosting’s Role in Website Structure & SEO
Your hosting environment directly impacts crawl efficiency and structural performance.
Server Response Time
High TTFB slows crawling and indexing.
Cloud vs Shared Hosting
Cloud hosting offers:
- Better uptime
- Scalability
- Faster response times
Compare hosting types here: Cloud Hosting vs Shared Hosting
CDN & Caching
Content Delivery Networks reduce latency and improve Core Web Vitals.
HTTP/2 & HTTP/3
Modern protocols enhance loading efficiency.
Uptime & Crawl Budget
Frequent downtime causes indexing delays and ranking drops.
Use Google PageSpeed Insights to measure structural and speed performance.
Mobile-Friendly & Responsive Architecture
With mobile-first indexing, structure must prioritise mobile UX.
Key Elements
- Responsive design
- Fast-loading mobile pages
- Clear mobile navigation
- Optimised tap targets
Avoid separate m-dot versions unless necessary.
Common Website Structure Mistakes
- Orphan pages
- Broken internal links
- Duplicate categories
- Excessive nested folders
- No canonical tags
- Mixed HTTP and HTTPS versions
- No breadcrumb navigation
How to Audit Your Website Structure
- Crawl your site using SEO tools
- Analyse click depth
- Identify orphan content
- Fix redirect chains
- Review internal linking distribution
- Check sitemap accuracy
A strong structure improves crawl efficiency and indexing consistency.
Example of a Perfect SEO Website Structure
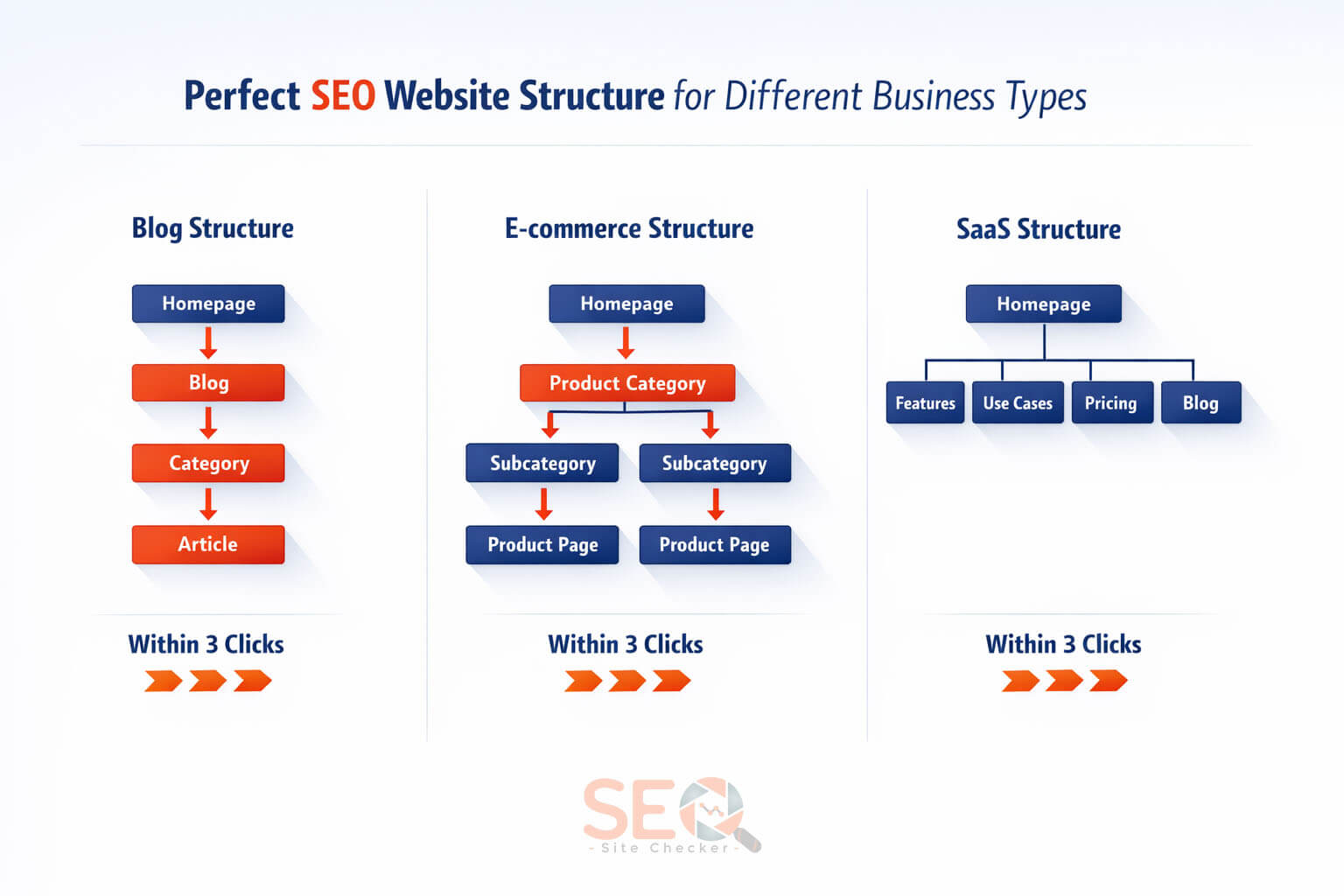
Blog Structure
Homepage
→ Blog
→ Category
→ Article
E-commerce Structure
Homepage
→ Product Category
→ Subcategory
→ Product Page
SaaS Structure
Homepage
→ Features
→ Use Cases
→ Pricing
→ Blog
All key pages within 3 clicks.
Final Thoughts
An SEO-friendly website structure is not optional, it’s foundational.
You can produce exceptional content, but without clean architecture, strong internal linking, and technically optimised hosting, rankings will plateau.
Start with hierarchy.
Optimise URLs.
Strengthen internal links.
Upgrade hosting if necessary.
Audit regularly.
Structure is strategy. And strategy wins rankings.
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) is a list of common questions and answers provided to quickly address common concerns or inquiries.
What is an SEO-friendly website structure?
How do I structure my website for SEO?
Does website structure affect ranking?
What is the best URL structure for SEO?
What is a flat website structure?
Is breadcrumb navigation good for SEO?
How does hosting affect website structure?
.png)
