Flat vs Deep Website Structure

Introduction: Why Website Structure Still Matters in 2026
Website structure isn’t just about organizing pages. It directly impacts how search engines crawl your site, how authority flows between pages, and how easily users can find what they need.
In 2026, Google’s algorithms are smarter than ever but they still rely on clean, logical site architecture to understand content relationships. If your structure is messy or overly complex, even great content can struggle to rank.
Choosing between a flat and deep website structure is one of the most important decisions in technical SEO.
If you're building or restructuring a site, you should first understand the fundamentals of a seo friendly website structure and follow a solid proper site architecture framework. For a deeper breakdown of technical foundations, you can also review this technical SEO structure guide.
Now let’s break down the two core models.
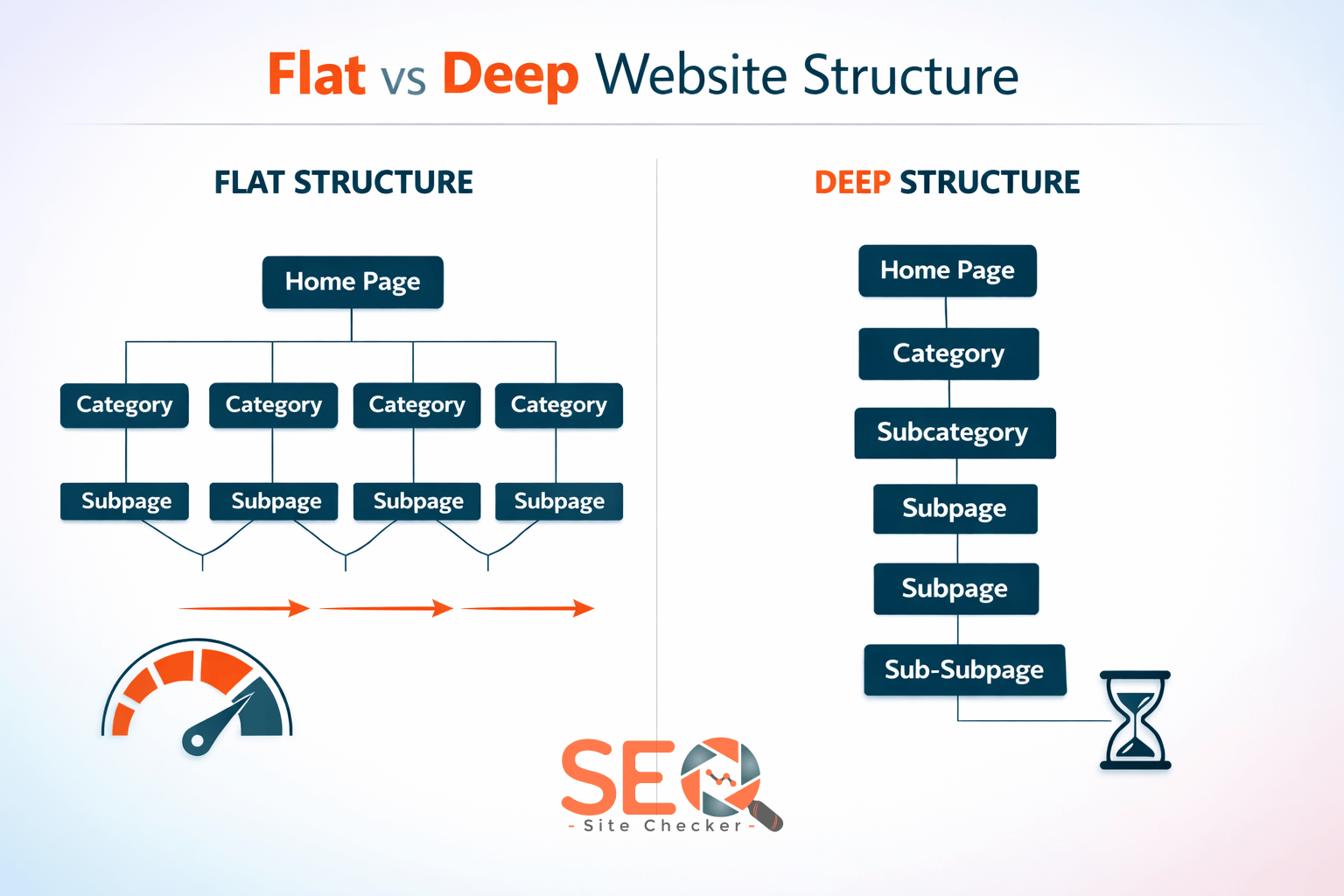
What Is Flat Website Architecture?
A flat website structure (also called shallow architecture) ensures that most important pages are accessible within three clicks or fewer from the homepage.
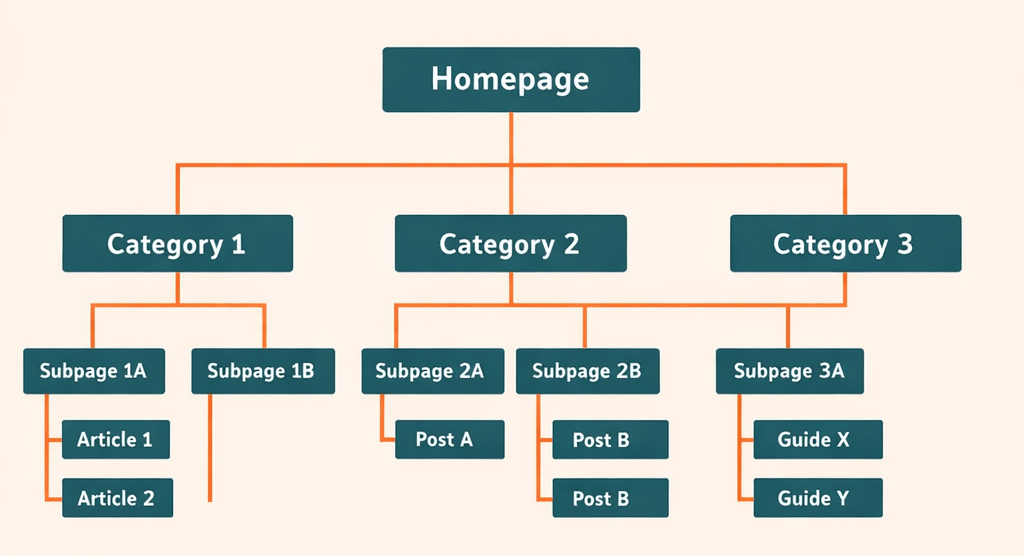
Simple Example:
Homepage
→ Category
→ Page
That’s it. Minimal layers. Direct access.
Key Characteristics of Flat Architecture
- Low click depth
- Strong internal linking
- Short, clean URLs
- Minimal nested subfolders
- Clear content hierarchy
Why SEO Experts Prefer Flat Structures
Flat architecture improves:
- Crawl efficiency
- Indexing speed
- Link equity distribution
- User experience
When pages are closer to the homepage, they receive stronger authority signals. Googlebot can discover them faster and revisit them more frequently.
Ideal Use Cases
Flat structures work best for:
- Blogs
- SaaS websites
- Local business websites
- Service-based websites
- Small to medium-sized content sites
For example, a digital marketing agency with 50–150 pages should prioritize a shallow hierarchy rather than burying services under five layers of categories.
What Is Deep Website Architecture?
A deep website structure contains multiple layers of categories and subcategories before reaching a final page.
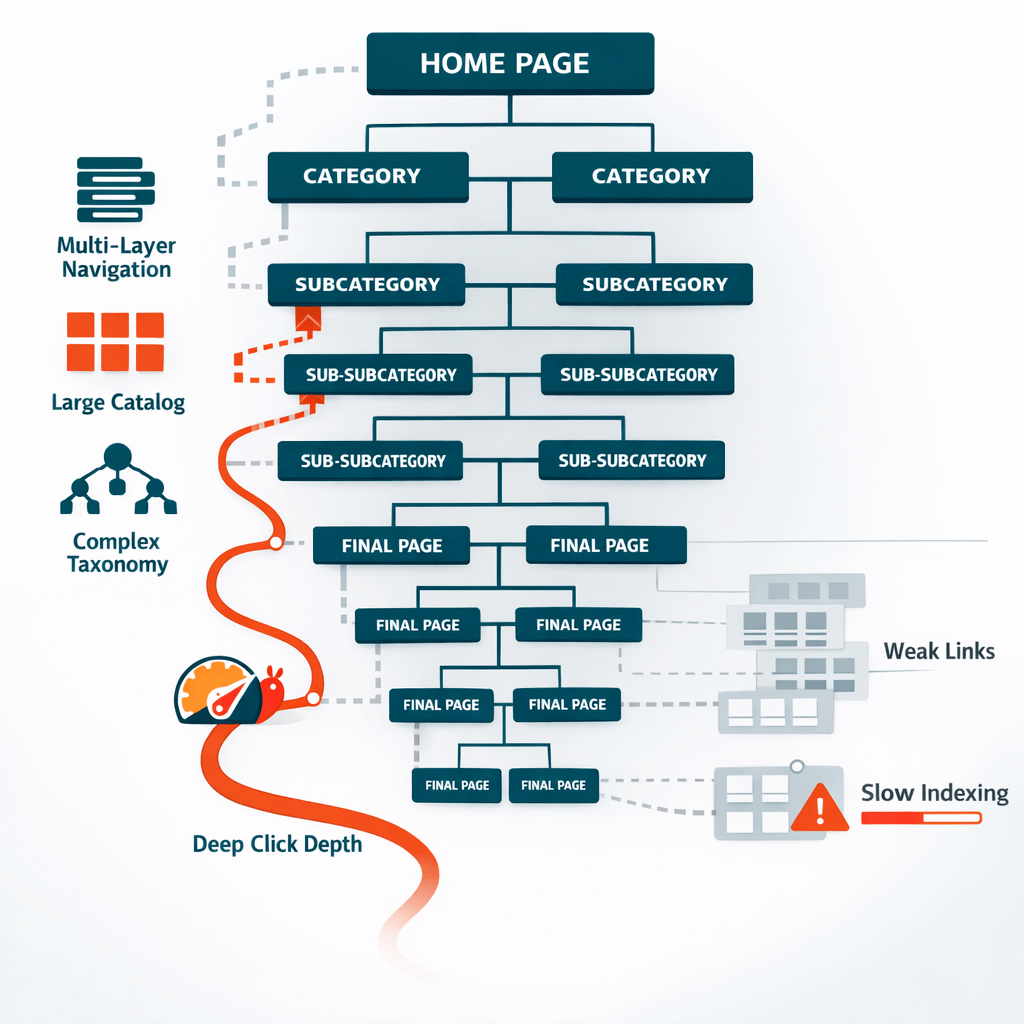
Example:
Homepage
→ Category
→ Subcategory
→ Sub-subcategory
→ Page
Now your content sits 4-6 clicks deep.
Key Characteristics of Deep Architecture
- High click depth
- Complex taxonomy
- Multi-layer navigation
- Often used for large catalogs
- Frequently seen in enterprise eCommerce
When Deep Structure Makes Sense
Deep architecture is sometimes necessary for:
- Large eCommerce stores (10,000+ products)
- Enterprise-level publishing platforms
- Large news websites
- Complex marketplace platforms
However, without careful internal linking, deep structures can create serious SEO problems.
The Risks
- Buried pages get less authority
- Crawl budget inefficiencies
- Slower indexation
- Orphaned pages
- Weak internal link equity flow
If your site keeps expanding without strategic architecture planning, your rankings may suffer over time.
Crawl Budget Impact: Flat vs Deep Structure
What Is Crawl Budget?
Crawl budget refers to the number of pages Googlebot crawls on your site within a specific time frame.
According to Google’s official guidance on site structure (Google Search Central), crawl efficiency plays a major role in how quickly content gets indexed and updated.
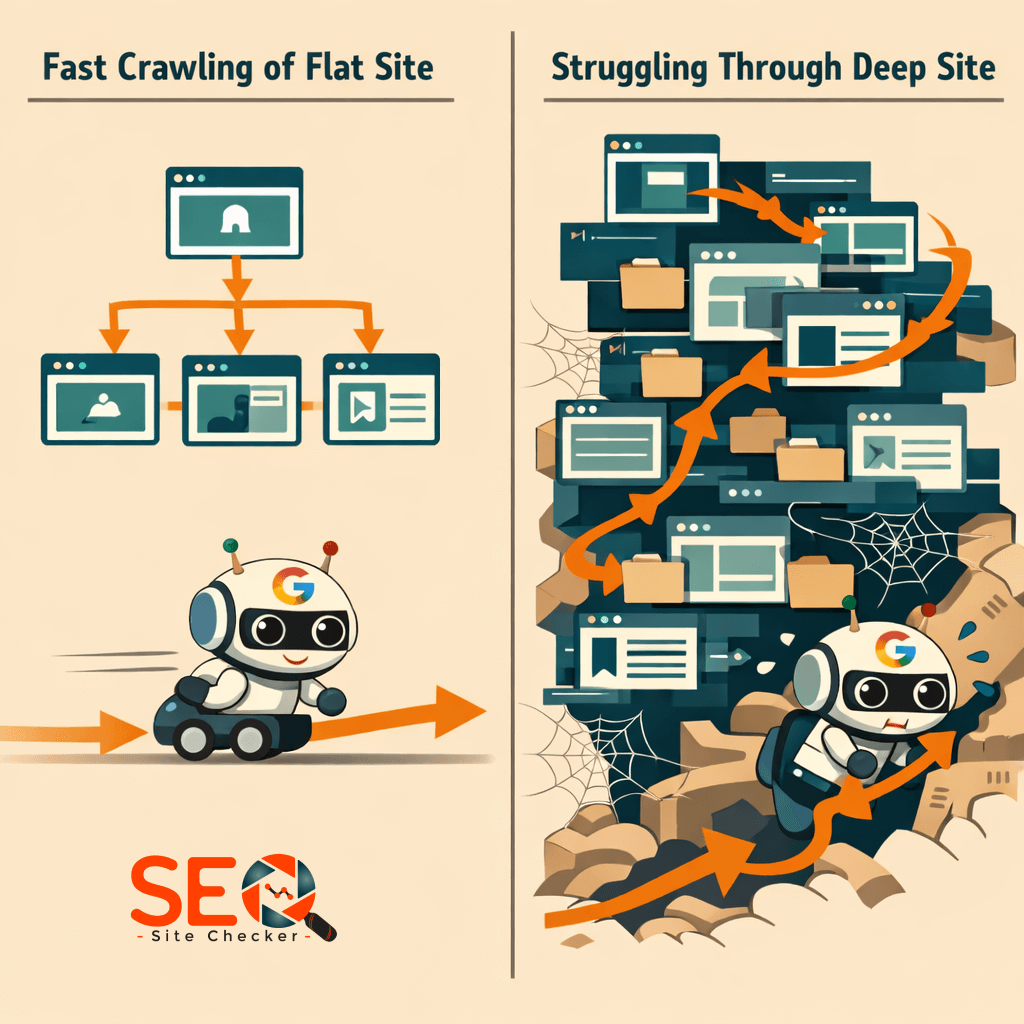
How Flat Structure Helps Crawl Budget
Flat architecture:
- Reduces unnecessary crawl paths
- Makes pages easier to discover
- Improves internal authority flow
- Helps new content get indexed faster
Googlebot doesn’t need to “dig” through layers.
How Deep Structure Can Hurt Crawl Budget
Deep sites often:
- Waste crawl budget on low-value filter URLs
- Create infinite category combinations
- Hide important content under unnecessary folders
This is especially dangerous for large sites.
If crawl budget gets wasted on thin or repetitive pages, important pages may not get crawled frequently.
Internal Link Depth Comparison
Click depth matters more than many website owners realize.
Studies and industry experts, including insights shared in internal linking best practices by Ahrefs, show that pages closer to the homepage tend to perform better.
Why?
Because internal links distribute authority (often called link equity).
In a flat structure:
- Authority spreads evenly.
- Important pages remain strong.
In a deep structure:
- Authority weakens as it passes through multiple layers.
- Deep pages receive diluted signals.
This is why modern SEO strategies use:
- Contextual internal links
- Hub-and-spoke models
- Topic clusters
- Strategic breadcrumb navigation
When properly implemented, even deeper sites can maintain strong authority flow but it requires careful planning.
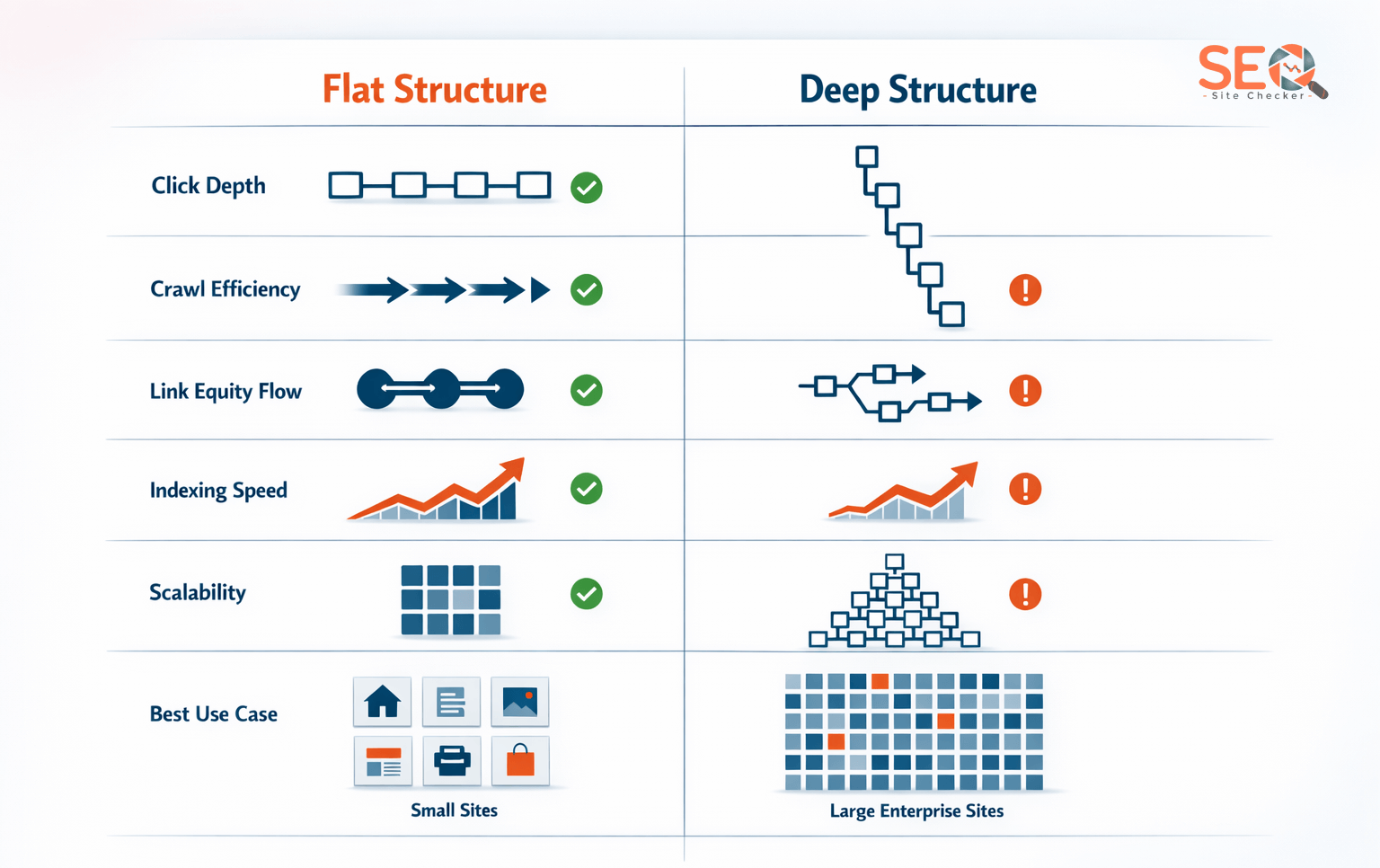
Flat vs Deep Website Structure: Comparison Table
| Feature | Flat Structure | Deep Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Click Depth | Low (1-3 clicks) | High (4+ clicks) |
| Crawl Efficiency | High | Moderate to Low |
| Link Equity Flow | Strong & Direct | Diluted |
| Indexing Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Scalability | Moderate | High |
| Best For | Small–Medium Sites | Enterprise & Large Catalogs |
Which Structure Is Better for SEO?
Short Answer:
Flat structure wins in most cases.
Detailed Answer:
For the majority of websites especially service businesses, blogs, SaaS, and local brands, flat architecture is superior.
It provides:
- Better crawlability
- Stronger authority signals
- Improved user experience
- Faster indexing
However, for massive eCommerce sites, a fully flat structure isn’t realistic. Instead, a controlled hybrid model works best.
That means:
- Keeping important pages within 3 clicks
- Limiting unnecessary subcategories
- Strengthening internal linking
The key isn’t “flat vs deep”.
The key is strategic structure with controlled depth.
Best Practices for Scaling Websites Without Going Too Deep
As your site grows, follow these rules:
1. Limit Hierarchy Levels
Try not to exceed 3-4 folder layers.
2. Build Topic Silos (Not Endless Subcategories)
Group related content logically.
3. Use Breadcrumb Navigation
Breadcrumbs:
- Improve user navigation
- Help search engines understand hierarchy
- Strengthen internal linking
4. Strengthen Internal Links
Every important page should receive contextual links from:
- Blog posts
- Service pages
- Resource pages
5. Monitor Click Depth Regularly
Use crawl tools to ensure important pages remain accessible.
For a complete breakdown of planning scalable architecture, revisit: SEO-Friendly Website Structure: Hosting & Technical Setup Guide
6-Step Implementation Guide
If you’re restructuring your site, follow this process:
Step 1: Audit Current Click Depth
Use a site crawler to identify pages buried 4+ clicks deep.
Step 2: Identify High-Value Pages
Focus on:
- Revenue pages
- High-traffic pages
- Core services
Step 3: Flatten Priority Pages
Add:
- Internal links from homepage
- Navigation links
- Sidebar links
- Footer links
Step 4: Simplify URLs
Avoid unnecessary folder nesting.
Bad example:
example.com/category/subcategory/sub-subcategory/page
Better:
example.com/category/page
Step 5: Strengthen Internal Linking System
Build topic clusters around pillar pages to maintain authority flow.
Common Website Structure Mistakes
Avoid these common SEO errors:
- Over-nesting categories
- Creating duplicate taxonomy pages
- Ignoring internal linking
- Leaving orphan pages
- Infinite filter URLs (common in eCommerce)
- Building navigation only for users, not crawlers
Remember:
Good UX and good SEO structure usually align.
Final Thoughts
Flat vs deep website structure isn’t just a theoretical debate.
It directly impacts:
- Rankings
- Crawl efficiency
- User experience
- Authority distribution
- Long-term scalability
If your goal is stronger rankings in 2026 and beyond, prioritize:
- Shallow hierarchy
- Strategic internal linking
- Clean taxonomy
- Logical content clusters
When in doubt, simplify.
Because in SEO, clarity wins.
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) is a list of common questions and answers provided to quickly address common concerns or inquiries.
Is flat website structure better for SEO?
What is considered a deep website structure?
How many clicks should a page be from the homepage?
Does site structure affect crawl budget?
What structure is best for large eCommerce sites?

